Top 10 Data Scientist Skills Should Learn in 2023
As the demand for data science expertise increases, the need for more data scientists to fulfill various job roles also increases. Although data science is a distinct discipline, it is not limited to any particular industry or business type. Data scientists have the potential to create significant impacts in multiple sectors and professional positions. For that reason, you need to learn these data scientist skills in 2023.
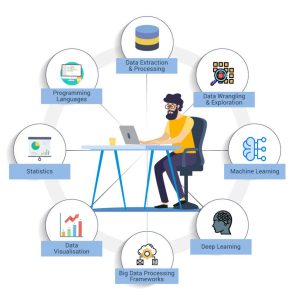
So, as you pursue your education in this field, be sure to focus on developing these core skills that will make you a well-rounded and valuable member of any team or organization. As an aspiring data scientist, it is important to recognize that education is the essential starting point on this career path. Apart from the technical components, there are a set of skills within the data science field which have broader applications across all subject areas. By practicing and fine-tuning these skills as well, one can stand out amongst other candidates looking to break into the industry. As the field expands, there is an increase in both individuals seeking employment and researchers studying it.
Non-Technical Skills
The abilities that are crucial for effectively applying data science to business issues will not necessitate as extensive technical instruction or official credentials. While technically proficient data scientists still require them, the soft skills and competencies listed below are essential for success in the field.
1. Critical thinking
With this skill, you will:
- To perform a thorough evaluation, it is important to objectively scrutinize the inquiries, Proposed explanations or predictions, and outcomes of a study.
- To solve a problem, it is essential to comprehend which resources are crucial.
- Examine issues from various angles and viewpoints.
Therefore, developing critical thinking skills should be an essential part of the training and education of data scientists. This will help them not only excel in their field but also contribute to the success of their organization by providing valuable insights that can inform key decisions. Rewritten: Proficiency in critical thinking is a highly advantageous ability that can be applied proficiently in any work field. The capacity to think critically is particularly crucial for data scientists as they must effectively formulate inquiries and grasp how the findings culminate from or impact a business to shape future endeavors. Given this, it is imperative that effective education and instruction on critical thinking form a fundamental component of a data scientist’s professional development in order for them to attain excellence in their profession and facilitate positive contributions towards organizational triumph by furnishing crucial insights for crucial determinations. Taking actions requires going through specific steps.
Before forming an opinion, it is crucial to conduct an impartial analysis of issues while handling data interpretations. In the realm of data science, critical thinking entails examining every aspect of a problem, taking into account the data source, and maintaining a sense of curiosity.
2. Effective communication
With this skill, you will:
- Describe the significance of data-based discoveries in language that is relevant to the world of business.
- Present information in a manner that emphasizes the importance of taking action.
- Describe the methodology and underlying beliefs that resulted in a decision.

Communication effectiveness is a highly valuable ability desired in virtually all fields. Whether occupying a starting role or holding the top position as CEO, being able to engage with others proves to be a beneficial attribute that aids in expediting task completion.
Therefore, communication skills are just as important as technical skills for data scientists in the business world. Data scientists must have the ability to comprehend complex data sets and then distill their findings into easy-to-understand insights that can be conveyed to different stakeholders within a company. This ultimately enables businesses to make more informed and data-driven decisions. When data provides solutions to diverse issues or responds to inquiries concerning business, companies will depend on data scientists who can offer solutions and communicate effectively to enable others to act appropriately.
3. Proactive problem solving
With this skill, you will:
- Recognize potential chances and clarify issues, as well as provide explanations for their resolutions.
- Learn how to tackle issues by discovering current presumptions and available assets.
- Don your detective guise and discern the optimal approaches to employ for obtaining accurate solutions.
Problem solving is a crucial aspect of data science and one cannot be a data scientist without possessing the necessary skills and willingness to solve problems. The main focus of data science revolves around problem-solving, but in order to excel at it, one must also have the drive to investigate thoroughly to find the underlying cause of an issue, in addition to having a solid approach towards developing solutions. Solvers can effortlessly detect complicated problems that may not be obvious at first and promptly shift focus to devising effective strategies for resolving them and determining the most optimal solutions.
4. Intellectual curiosity
With this skill, you will:
- Drive the search for answers
- Go beyond the superficial findings and preliminary conjectures.
- Be imaginative while having a strong thirst for knowledge.
- Continuously inquire with the question “why” as a single answer is often insufficient.

The ideal data scientist exhibits a passion for uncovering hidden patterns, trends and insights in data and will not be content with simply accepting the information on the surface. They are driven to ask new and unexpected questions that may reveal even greater insights, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of the information provided. Effective data scientists aim to uncover the fundamental truths beneath the data they study and are always striving for a deeper understanding. The search for solutions or explanations.
5. Business sense
With this skill, you will:
- Comprehend the requirements and individual demands of the organization.
- Understand the issues within the organization that require solutions and the reasons for resolving them.
- Reinterpret information so that it can be utilized in a productive manner that benefits the company.
Problems and make informed decisions based on the data. In other words, data scientists must have a comprehensive set of skills that combines knowledge about data and the industry they work in. Merely being proficient with statistics and analysis is not enough; data scientists must also possess a thorough understanding of the specific business needs and challenges they are trying to solve. Examine existing challenges and contemplate how data can aid future advancement and prosperity.

“Data science is more than just number crunching: it is the application of various skills to solve particular problems in an industry,” explains Dr. N. R. Srinivasa Raghavan, Chief Global Data Scientist at Infosys.
Technical skills
These are more required skills that you typically see listed closer to the top of job descriptions for data scientists. Many of the areas will be developed and covered in educational courses or formal business training. And many organizations are increasingly emphasizing them as their analytics and data staffs evolve.
6. Ability to prepare data for effective analysis
With this skill, you will:
- Collect, organize, analyze and structure information.
- Examine immense amounts of organized or unorganized information.
- Format and display information in an optimal manner to facilitate effective decision-making and problem-solving.

Preparation in order to effectively perform data analysis. This involves finding, transforming and cleaning data, all of which are essential steps before analyzing the data. Both analysts and data scientists consider this process a critical component of their task to enable effective analytics workflows. Understanding data preparation is essential for successful analysis regardless of the tool being used. The tasks involved in preparing data and their correlation with data science workflows are being discussed. Tableau Prep Builder is a user-friendly tool for all levels of expertise.
7. Ability to leverage self-service analytics platforms
With this skill, you will:
- Comprehend the advantages and obstacles of employing data representation techniques.
- Basic knowledge of market solutions
- Learn and utilize the most effective methods and strategies for developing analyses.
- The capacity to distribute outcomes through user-accessible dashboards or software.
This ability is categorized as a non-technical skill because it involves critical thinking and communication. Self-service analytics tools assist in displaying the outcomes of data science procedures and investigating the data, but they also aid in disseminating these findings to individuals with minimal technical expertise. If you make a dashboard using a self-service platform, the users at the end can adjust certain settings to explore their own queries and see how they affect the analysis in real-time as updates are made to the dashboard.
8. Ability to write efficient and maintainable code
With this skill, you will:
- Interact with the software that is responsible for examining, interpreting, and displaying information without any intermediaries involved.
- Develop software or instructions to analyze information systematically.
- Collect and prepare data through APIs
Being adept at this skill is crucial for data scientists as they are heavily involved with systems that are intended for analyzing and managing data. Consequently, they also need to have a comprehensive understanding of the inner workings of these systems. As there are various programming languages utilized in data science, it is important to acquire and utilize the languages that are relevant to one’s particular role. Challenges faced by the industry and businesses.
9. Ability to apply math and statistics appropriately
With this skill, you will:
- Explore the data and discover significant patterns and connections.
- Utilize a precise and thorough approach to statistical analysis in order to distinguish relevant information from irrelevant background phenomena.
- Comprehend the advantages and drawbacks of diverse testing methodologies and their appropriateness for a specific issue.
In the field of data science, just as in coding, mathematics and statistics are essential. Data scientists work with statistical and mathematical models, and are required to not only apply them but also enhance their functionality. Proficiency in statistics is crucial for data scientists as it allows them to scrutinize various types of data with a critical eye. The paragraph discusses the capabilities of analytics in addressing various issues and the limitations of its capacity. There are situations when unique approaches must be developed by merging or adjusting existing analytical methods and instruments. A comprehensive comprehension of the foundations and procedures is essential for efficiently using these applications.
10. Ability to leverage machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI)
With this skill, you will:
- Comprehend the appropriate timing and circumstances for implementing machine learning and AI in a business setting.
- Develop and distribute models to effectively execute useful artificial intelligence solutions.
- Provide an explanation of models and predictions that is relevant and practical for the business context.
We need to recognize that they will not replace human roles in most organizations. Rather, they will augment our abilities and enable us to provide even greater value as data scientists. As a recent statement by a Chief Data Officer indicates, incorporating these technologies into our work practices can help us operate more efficiently and effectively.” In order to excel in AI, it is crucial to possess several innate human abilities. The biggest obstacle in AI lies in determining whether the available data is appropriate or not, since the seemingly “correct” data may still provide inaccurate results. Additionally, it is necessary to choose data that is “good enough” for AI before training the algorithm. The most beneficial pattern to use.
