Corona Virus Awareness: Employer vs. Employee

News that cases of the recently distinguished 2019 Novel Coronavirus (also stated as COVID-19, 2019-nCoV, or SARS-CoV-2, but more commonly known simply as the “Coronavirus”) still spreading and now 130 countries in the world are infected.
The virus was first reported on Dec. 31 in Wuhan, Hubei province, China. There have been more than 135,467 confirmed cases now; the vast majority of the cases are in China. The vaccine is invented but not used in public yet.
The employers have looked for ways to protect their staff and organizations throughout what the World Health Organization has declared a global crisis. Company owners are thinking about employee safety and ways to address disease prevention in the workplace.
Bangladesh is facing a high risk of being influenced by the novel coronavirus outbreak as the virus has already spread in lots of places around the globe. And finally turning public fears into reality, authorities in Bangladesh have confirmed the first three patients of Covid-19, a new strain of coronavirus that has killed over 3,600 people around the world.
At this time, the case is evolving, and it is never too early for employers to think about how they can address employee concerns, cooperate to prevent an outbreak, or address one if it occurs. Employers ought to even be attentive to legal pitfalls that they may encounter when trying to protect their employees from the coronavirus.

Employers should also note that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) of the US government considers coronavirus a serious public health concern and has released guidance specifically addressed to organizations outlining recommendations and best practices on ensuring the working environment. The CDC also has released specific guidance for the healthcare industry, airline industry, IT industry, and other industries as it relates to the Coronavirus.
UNICEF Bangladesh also has released guidance specifically addressed to Bangladeshi people. Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina also asked the people not to be worried about the coronavirus as the country was able to handle this disease. For the past few days, IEDCR has been underlining cautiousness and improvement of individual cleanliness.
What is the Coronavirus and The Way It Is Transmitted?
Coronaviruses are an enormous family of viruses that are normal in people and lots of different species of animals, including cows, camels, cats, and bats. Rarely, animal coronaviruses can influence people and then transmit between people, such as with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV. The infection that causes COVID-19 is spreading from person to person in China and some constrained person-to-person transmission has been accounted in countries outside China, including the United States of America. Like other respiratory diseases like seasonal influenza are currently widespread in many countries.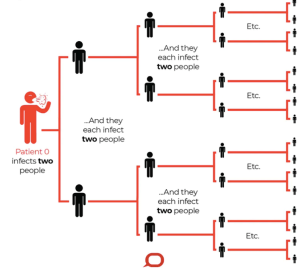
How dangerous is it?
Like other respiratory illnesses, it can cause delicate symptoms as well as a sore throat, runny nose, cough, and fever. It may be severe for some people and can prompt pneumonia breathing challenges and organ failure. More rarely, the disease can be fatal. Older citizens and people with pre-existing medical conditions seem to be more vulnerable to becoming severely sick with the virus.
What Are the Primary Symptoms of the Coronavirus?
People infected with the novel coronavirus usually show a number of common signs and symptoms, which include fever, difficulty in breathing, and cough, similar to many other respiratory illnesses, and can cause pneumonia, kidney failure, and even death.

Older men and people with other medical problems (such as diabetes, asthma, or heart disease) possibly more vulnerable to be getting seriously sick.
How will unfold of the Coronavirus Be Prevented?
Experience says taking precautionary measures, remaining vigilant, and preparing are key. There is currently no vaccine to prevent coronavirus disease (COVID-19).
Standard recommendations to stop infection spread include:
- Clean hands frequently with alcohol-based hand rub or soap and water
- Cover nose and mouth when coughing and sneezing with tissue or flexed elbow
- Avoid close contact (4 meters or 13 feet) with anybody with cold or influenza-like side effects
- If you go to the market, don’t touch animals or anything in the zone they stay
- Go to the hospital near you if you have a fever, cough or feel that it is difficult to breathe.

What should Employers Do to Take Care of a Secure Workplace?
Given that employers have a legal obligation to produce a secure workplace for employees, employers ought to assist in preventing the spread of disease and keep staff healthy:
- Educating staff on the signs and symptoms of the coronavirus and the precautions that can be taken to limit the risk of getting the infection.
- Giving hand sanitizer and hand washing stations, flu masks, and facial tissues; encouraging employees to wash hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds; and cleaning and purifying regularly touched objects and surfaces.
- Limiting unnecessary conferences, meetings, and visitors, and assessing the risks of exposure by recognizing staff who may have recently traveled to, come in direct contact with, or are scheduled to go to virus infected country.
- Implementing and/or potentially assessing workplace crisis response protocols.
- Providing travel guidelines for travel abroad or domestically.
- Permitting sick staff to work from home or take leave as appropriate.

What should a workplace Novel Coronavirus response plan cover?
The plan should affect the following:
Before an Epidemic
Preventive measures. The Centre for Health Protection gave Health Advice on the Prevention of Severe Respiratory Disease related to a Novel Infectious Agent in the Workplace, which sets out the rules on preventive measures that will be taken.
- Sanitizing the workplace regularly.
- Keeping up good indoor ventilation.
- Ensuring that employees are aware of the employer’s plans in the event of an outbreak.
- Guaranteeing adequate supplies of appropriate masks, alcohol wipes, gloves, paper towels, thermometers, disinfectants, and so on.

During an Epidemic
The steps the employer will take to ensure the safety of staff while at work during the Novel Coronavirus outbreak including how an employer will recognize the risks of employees getting infected and how to minimize such risks.
- Communication strategies, for example, how and what data will be conveyed to workers, providers, and clients.
- Where workers will work, e.g., at home, in the office or in different temporary offices.
- At what stage will the workplace be shut and who will conclude that?
- How to manage the infected colleagues, e.g., counseling.
- What to do with high-risk/exposure employees (e.g., pregnant, key staff, and employees who travel)
After an Epidemic
Approaches to guarantee that employees have fully recovered before they are permitted again into the workplace.
Rehabilitation for sick staff coming back to the workplace.
Correspondence with employees and adaptability in enforcing requirements imposed on employees under their agreement of employment will be important in maintaining employee relations and reducing anxiety and panic during an outbreak. Therefore, depending on the conditions, employers may wish to:
- Discuss with employees about the possibility of a workplace closure prior to closing;
- Permit staff to take annual leave or unpaid leave once sick leave has been exhausted;
- Permit employees to work from home; and
- Explore salary reduction or unpaid leave as an alternative to termination of employment where business has slowed down.
- Employers should make visitors to their offices aware of any health and safety hazards associated with entering the workplace before any intended visit, where reasonably practicable.

Stay safe and Pray for Others.
Author
Shahriar Ibne Azam, Sr. Digital Marketing Specialist
sazam@insightintechnology.azurewebsites.net
